The California Public Utilities Commission has issued a proposed decision that calls for a monthly fixed charge of $24 for most customers. There is no basis in economic principles that calls for collecting “fixed costs” (too often misidentified) in a fixed charge. This so-called principle gets confused with the second-best solution for regulated monopoly pricing where the monopoly has declining marginal costs that are below average costs which has a two part tariff of a lump sum payment and variable prices at marginal costs. (And Ramsey pricing, which California uses a derivative of that in equal percent marginal cost (EPMC) allocation, also is a second-best efficient pricing method that relies solely on volumetric units.) The evidence for a natural monopoly is that average costs are falling over time as sales expand.
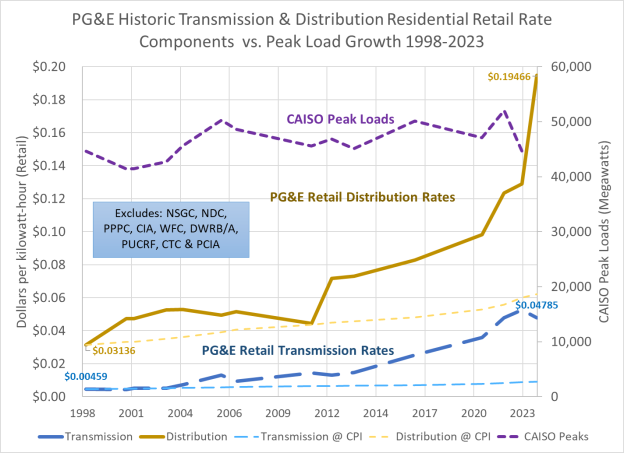
However, as shown by the chart above for PG&E’s distribution and transmission (and SCE’s looks similar), average costs as represented in retail rates are rising. This means that marginal costs must be above average costs. (If this isn’t true then a fully detailed explanation is required—none has been presented so far.) The conditions for regulated monopoly pricing with a lump sum or fixed charge component do not exist in California.
Using the logic that fixed costs should be collected through fixed charges, then the marketplace would be rife with all sorts of entry, access and connection fees at grocery stores, nail salons and other retail outlets as well as restaurants, car dealers, etc. to cover the costs of ownership and leases, operational overhead and other invariant costs. Simply put that’s not the case. All of those producers and providers price on a per unit basis because that’s how a competitive market works. In those markets, customers have the ability to choose and move among sellers, so the seller is forced to recover costs on a single unit price. You might respond, well, cell providers have monthly fixed charges. But that’s not true—those are monthly connection fees that represent the marginal cost of interconnecting to a network. And customers have the option of switching (and many do) to a provider with a lower monthly fee. The unit of consumption is interconnection, which is a longer period than the single momentary instance that economists love because they can use calculus to derive it.
Utility regulation is supposed to mimic the outcome of competitive markets, including pricing patterns. That means that fixed cost recovery through a fixed charge must be limited to a customer-dedicated facility which cannot be used by another customer. That would be the service connection, which has a monthly investment recovery cost of about $10 to $15/month. Everything else must be priced on a volumetric basis as would be in a competitive market. (And the rise of DERs is now introducing true competition into this marketplace.)
The problem is that we’re missing the other key aspect of competitive markets—that investors risk losing their investments due to poor management decisions. Virtually all of the excess stranded costs for California IOUs are due poor management, not “state mandates.” You can look at the differences between in-state IOU and muni rates to see the evidence. (And that an IOU has been convicted of killing nearly 100 people due to malfeasance further supports that conclusion.)
There are alternative solutions to California’s current dilemma but utility shareholders must accept their portion of the financial burden. Right now they are shielded completely as evidenced by record profits and rising share prices.